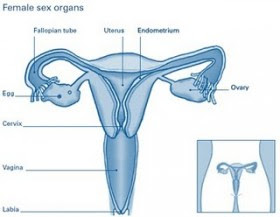
Female Sexual Organs Anatomy - Reproduction is an organ that serves to breed and produce offspring. In human reproduction also serves as a tool to achieve sexual pleasure. Because the man is called a sexual being.
Male sexual organ is different from female sexual organ. In our article this time we will only discuss the anatomy of the female reproductive organs and their functions.
The main purpose of the female sexual organ is to produce eggs and store them in the womb, waiting until a successful sperm cell fertilizes it.
The parts of the female reproductive organs are as follows:
1. Uterus or womb
The uterus is the female sexual organ which is hollow and shaped like a pear. The uterus or womb is a developing fetus during pregnancy. Therefore, the function of the uterus size can be enlarged up to 50 cm during pregnancy until birth.
2. Two of the fallopian tubes (fallopian tubes)
The fallopian tubes are a pair of tubes that were on each side, extending from the ovaries to the womb (uterus). This tube-shaped channel function to bring eggs from one of the ovaries (ovarian) every month, moving slowly toward the uterus.
3. Ovary
The ovaries are glands that produce female sex hormones and produce eggs or ova. Each ovary is sized only as big as almonds but containing 150,000 to 200,000 eggs.
Each month, from the time a woman is experiencing puberty to menopause, one ovary releases one egg (sometimes more, but not a common occurrence). The size of each egg is similar to the size of the head of a pin. The time when the egg is released is called ovulation.
4. Cervix
The female sexual organ function to produce mucus. The cervix connects the uterus to the lower part of the vagina. In the days leading up to ovulation, the mucus is more felt, elastic and smooth. During sexual intercourse took place, mucus helps the sperm of a man reaching the uterus and fallopian tubes.
5. Vulva
The vulva is the external female genitalia. Which is part of the vulva is pubic hair, pussy lips inner and outer (labia), the clitoris and the vaginal opening and the urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder.
6. The outer labia
Also called the labia majora are fleshy lips which cover the vulva. Outer labia contains sweat glands and the growth of pubic hair in the vagina.
7. The inner labia (labia minora)
That folds of skin that protect the entrance to the vagina and urethra. The inner labia sealed by the outer labia. Labia every woman is different in shape and size.
8. clitoris
The clitoris is the female sexual organ which is very sensitive to stimulation. The location is at the top of the urethra. Part of the clitoris that you can see only the edges only. The clitoris has many sensitive nerves so that when a woman is aroused, the clitoris will fill with blood and swell.
When the clitoris stroked or touched will give rise to a sense of fun. The feeling can create incredible sensation called an orgasm.
9. Vagina
Vagina including the inside of the female reproductive organs, about 9 cm long and leads from the cervix to the outside of the body. When a woman is menstruating, menstrual fluid out of the body through the vagina. The vagina is a space through which the baby was born. The vagina is also a space to enter the penis when sexual intercourse takes place.
The female reproductive system is more complicated than men because women have a uterus in which the baby during pregnancy until birth. Maintaining the health of the sexual organs is essential in order to egg production still occurs, regularly and can be fertilized by a sperm.
The female sexual organ is more complicated than in the male sexual organs for organ functions are also associated with reproductive function of sex takes place, pregnancy until birth.
Women health treatments and cure menorrhagia, menstrual flow and related symptoms that can cause uterine fibroids, prevent their recurrence.
Recents
Popular
-
On the previous post we've wrote an article about Knowing Uterine Fibroids . And this is its continuation, an important thing for you to...
-
What is the Uterine Fibroids ? Uterine fibroids is a standard health concern among a significant population of women. female internal rep...
-
Semen is a white fluid that comes out when a man ejaculates. Usually semen comes out in liquid form, can be condensed and can also dilute, ...
-
At the previous post we wrote about What causes Uterine Fibroids , you can read here ! . At this time we let you know the Symptoms of Uterin...
-
Cyst Uterus Tumor & Miscarriages, How big the risks? - Miscarriage is one of the issues that horrible pregnancy. Many women warned caut...
-
The Natural Remedies for Uterine Fibroids: Despite a long standing faith in the power of allopathic medication and other conventional form...
-
The biggest changes that occur when the growth is the onset of menstruation . Menstruation is a slight discharge of blood from the vagina fo...
-
Female Sexual Organs Anatomy - Reproduction is an organ that serves to breed and produce offspring. In human reproduction also serves as a ...
-
Another Causes Menorrhagia - Some cases of heavy bleeding during menstruation can not be known with certainty but some conditions cause meno...
-
Menorrhagia or Heavy Menstrual Flow (menstrual blood too much) is the term for excessive menstrual bleeding that is losing more than 80ml ...